In this Blog, we will get to know what Linux Files are and their uses. We will mainly focus on the files that are in Root directories, which contain many different files and directories. how we use them and what is stored init.
What is the Linux File System?
Linux file system is generally a built-in layer of a Linux operating system used to handle the data management of the storage. It helps to arrange the file on the disk storage. It manages the file name, file size, creation date, and much more information about a file. If we have an unsupported file format in our file system, we can download software to deal with it.
Let's go to Root Directories
So we know that the "ls" list command will tell us all the stuff in our current working directory. We also learn cd we can change directories to something else that we’re not like cd desktop now we’re in the desktop if I type in “pwd” it’ll also tell me where I am I’m in desktop because we just went there and we even saw that we type in cd .. it’ll take us back so now we’re back where we started and but if we going cd .. cd.. cd.. we go back and back until we can’t go back anymore which is where we’re at right now “/” that’s a root if I type in “pwd” that’s where we are the root of the file system that’s where it all started and that’s where we’re beginning our Blog Today.
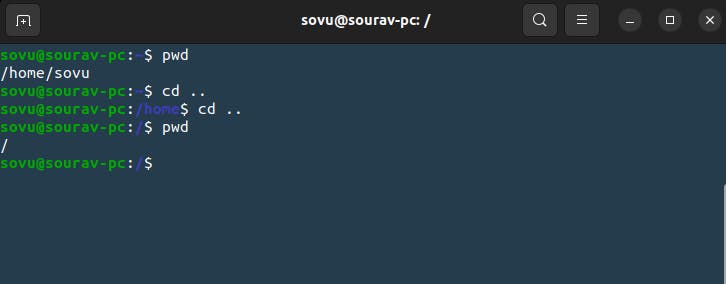
So what’s at the root of the file system
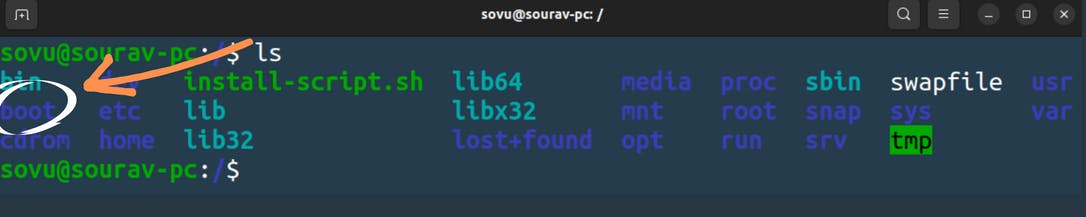
let’s see go ahead and type in "ls" as you can see below we have a lot of files and folders
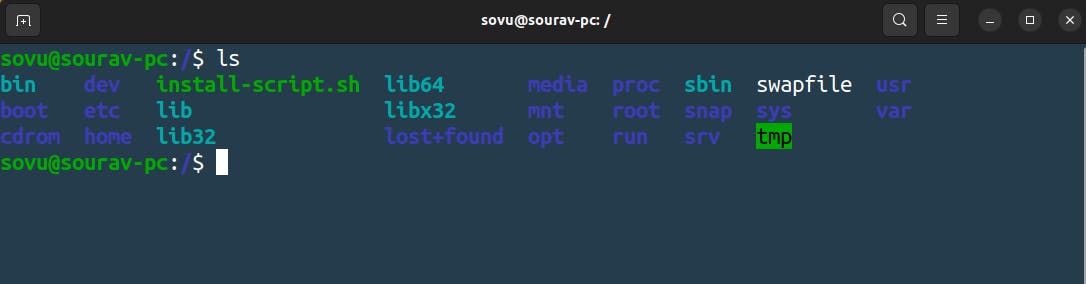
Let's start and go check one by one what are they and what are they doing
Everything I mean Everything in Linux is a file. literally, everything like configuration like your network setting thing like your IP address and all that interface its file. Devices like your hard drives, printers, and cd-roms all files are represented in a file in Linux
Now even more shocking and crazy is that the commands that we use are files “ls” and all the commands are files. Why don’t I just show you let’s go?
/bin
In the first directory(the directory you can say that it's a folder) you will see that is a bin. the full name of the bin is binaries. let's go into din directory or folder we’ll do “cd bin” to jump in there. Inside the bin directory or folder are the command binaries. know type “ls” command to list all the contents that are in the bin directory.
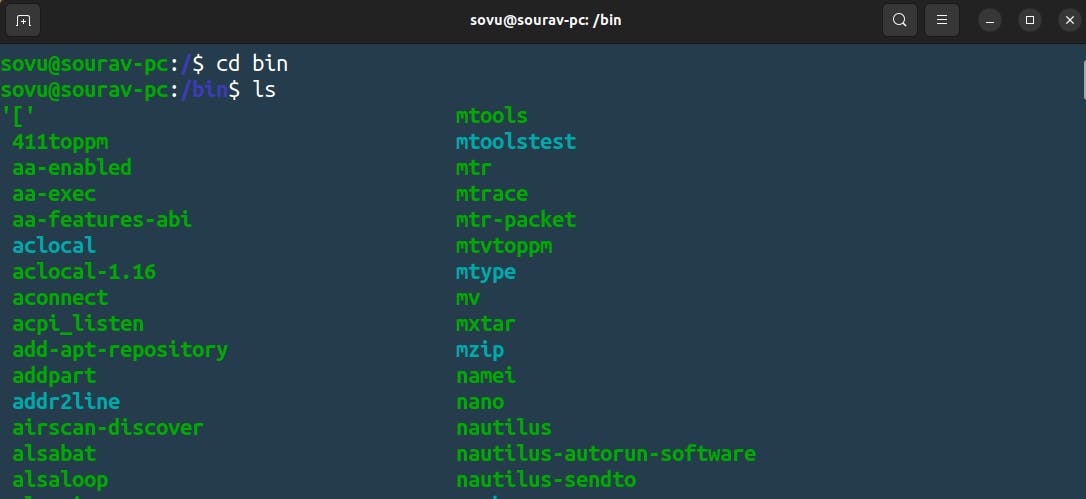
Here there are a lot of commands you’ll end up using in Linux in fact within the bin directory are essential command binaries so let’s scroll up and let’s find out “ls”.
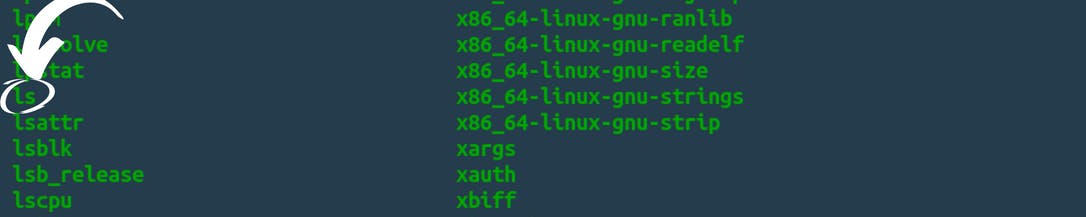
As you can see that “ls” command is nothing but just a file as I said in Linux everything is a file. Let's use the command “cat” to see what’s init
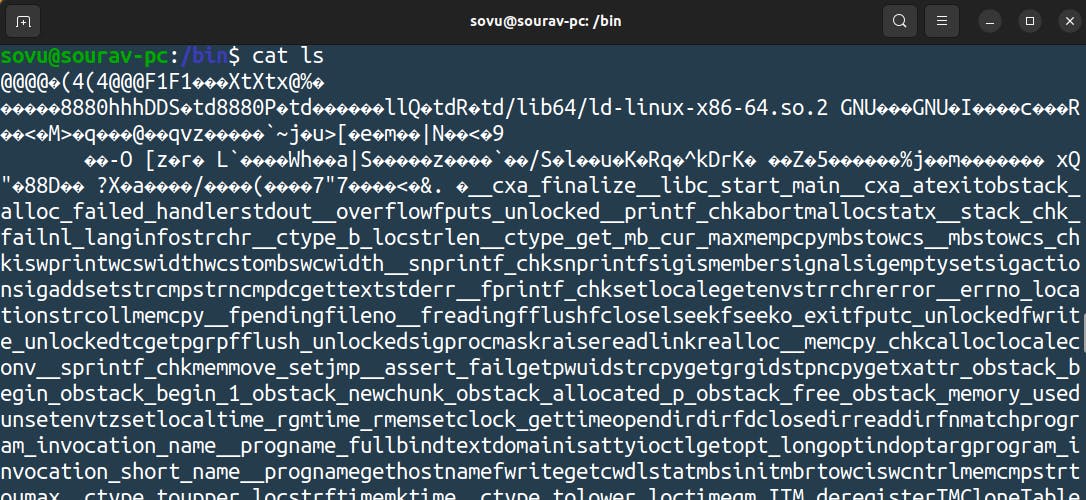
Do you understand any of this if you do you might be a robot but anyways you should not understand this it’s the command binary when you type in “ls” this is what it tells the computer to do.
So bin got all the essential commands like “cp” command to copy, “rm" command to remove, “cat” command and etc
/sbin
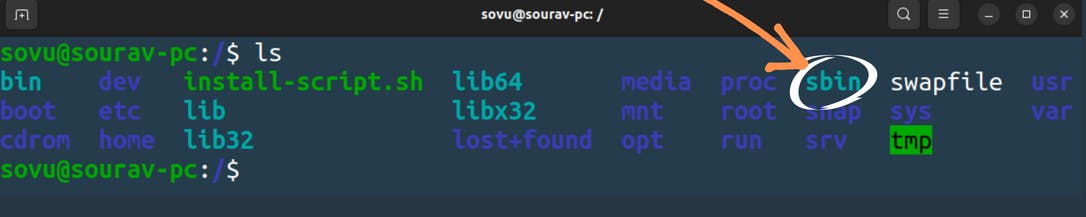 Now if go back to our root file and list the content we’ll see another directory that is sbin. which I like to call the super bin it is just like the bin but a bit more special you see super bin has special commands that only administrators would use to administer the system. so let's go into the super bin.
Now if go back to our root file and list the content we’ll see another directory that is sbin. which I like to call the super bin it is just like the bin but a bit more special you see super bin has special commands that only administrators would use to administer the system. so let's go into the super bin.
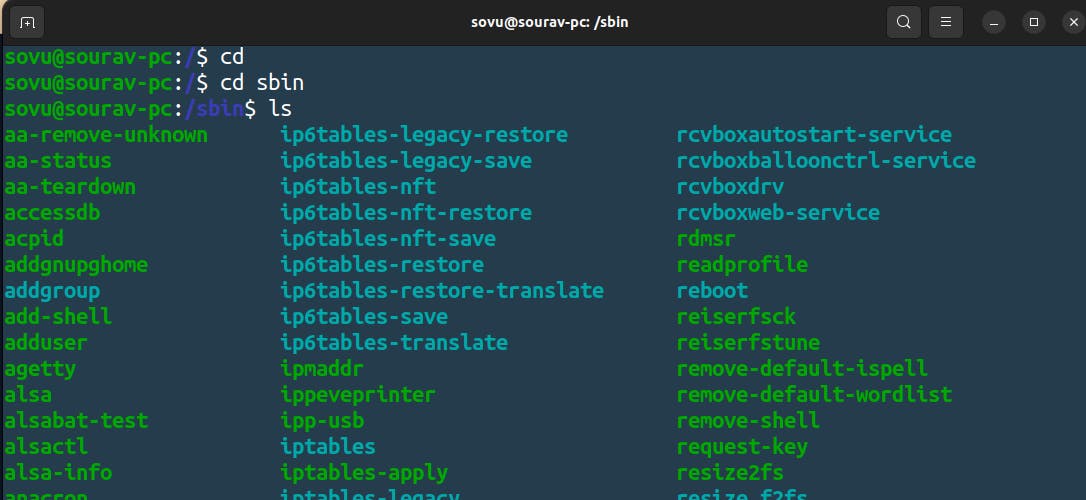
we can see all the super commands or we can say top-secret commands that only the administrators can use.
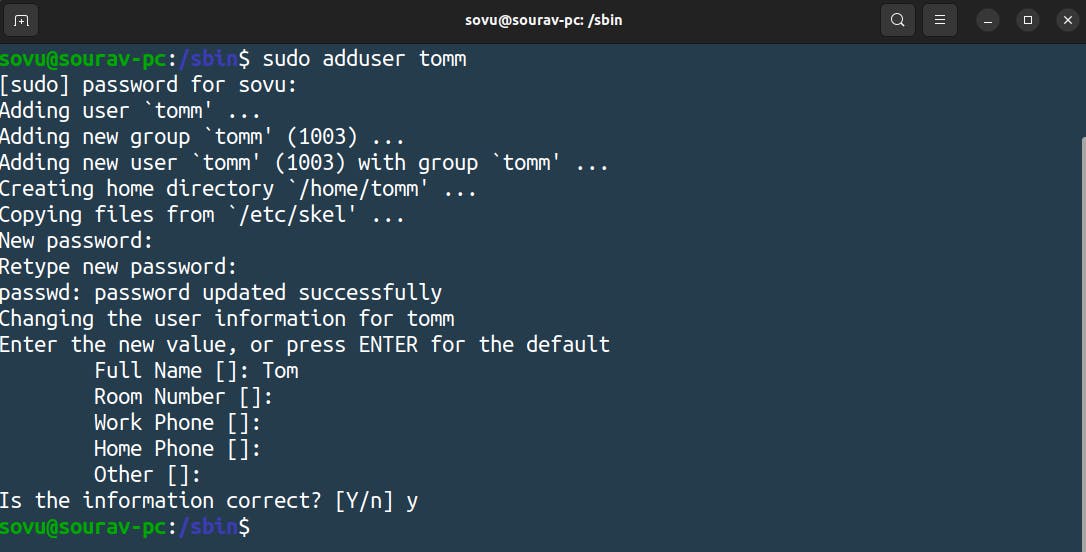
Let’s use one of the commands that are in sbin. we’ll use the “adduser” commands which help to add new users to our system.
/usr
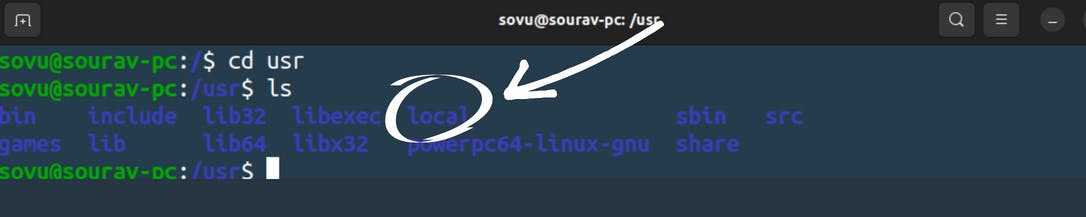
 Now let's go and see in your user directory. “cd usr” and “ls” .
Now let's go and see in your user directory. “cd usr” and “ls” .
Now notice something kind of strange. inside the usr directory or the user directory, we also have a bin and a sbin. so what going on here we just saw in the root directory then why are they are here again. let take a look inside “cd bin”
As you can see it has the same file as he has seen in the root’s bin let’s also check the sbin of usr
same as the previous sbin directory.
what’s going on it seems like we have some imposters here which one is the real one bin in the root or bin usr so the answer is both they’re both real there’s actually a pretty interesting history as to why we have two locations. I’m not going to say about it here but it all comes down to hard drive space look it up but essentially the bin and sbin in the usr directory are the same as the bin and sbin in the root directory now bin and sbin in the usr directory will typically have more commands there but you will see a ton of overlap here so that begs the question when we use the ls command are we using the command stored in a bin in usr or bin root we can actually find out you want to try it let’s try it out
we’re going to type in the command “which” it’s going to help us figure out which is it. it in the bin from root or bin from usr let go in check
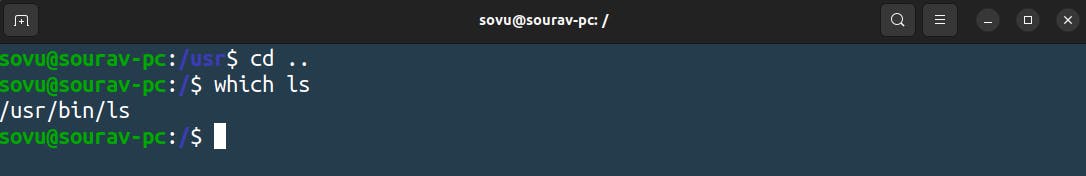
if you didn't catch on to what “which” command is doing you can use “which “ to find out where your command binaries.
let's go to usr directory and see another directory which is init
local
which is similar to ben and the super bin will store command binaries but it's here that you’ll want to store the command binaries that you might create.
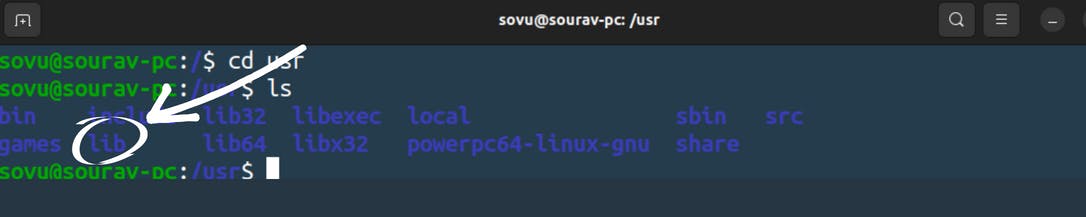
lib
lib has libraries that the command binaries will share
 And many other directories but we don’t use much.
And many other directories but we don’t use much.
/boot
 Boot what is that file your system needs to boot. boot files are self-explanatory. All the files your system needs to boot up how to boot up, and what drive to boot from.
Boot what is that file your system needs to boot. boot files are self-explanatory. All the files your system needs to boot up how to boot up, and what drive to boot from.
/var
 var have some things like a log file and also web application-related file. Our application gets installed in a bin folder we need to store the log file that is in var.
var have some things like a log file and also web application-related file. Our application gets installed in a bin folder we need to store the log file that is in var.
/tmp
 temporary files mean files are stored here which are temporary and will eventually go away after a system reboot.
temporary files mean files are stored here which are temporary and will eventually go away after a system reboot.
/lib
 We mentioned that bin is where our binaries and executables live, and lib is where you find the shared library files specifically things your system needs to boot.
We mentioned that bin is where our binaries and executables live, and lib is where you find the shared library files specifically things your system needs to boot.
/home
 Home is where you live home is where we live in fact it’s where every user lives on your system. let’s take a look inside
Home is where you live home is where we live in fact it’s where every user lives on your system. let’s take a look inside
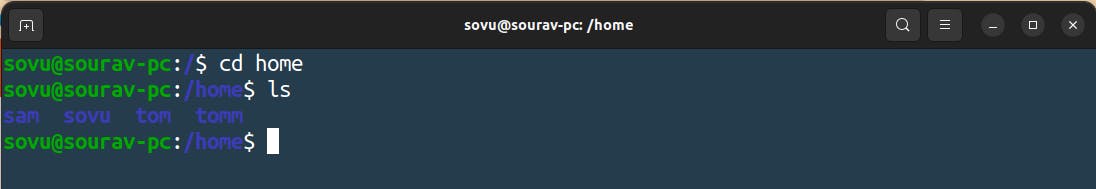
so we have to the user or we can say we have to home one is mine and other that we created in our above example so we can go in my home and see that we have so some folder and files that belong to me only.
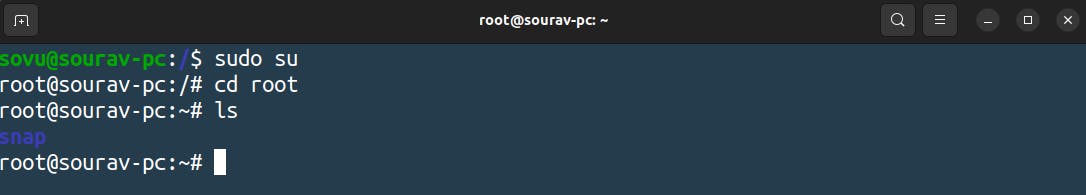
/root
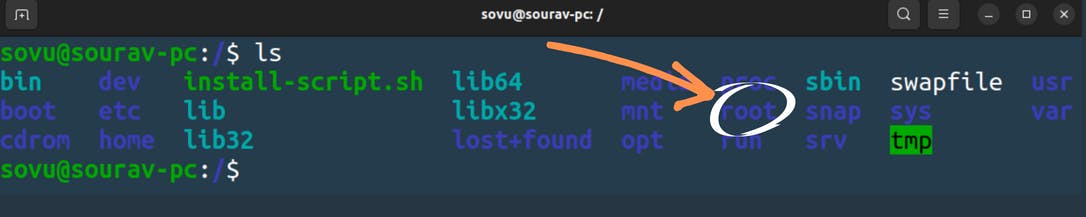 Now every Linux system has a root user but we didn’t see a home for the root where it lives because he wasn’t in this home.
Now every Linux system has a root user but we didn’t see a home for the root where it lives because he wasn’t in this home.
it has its own directory name root because he particular he lives somewhere else where people can’t bother him
/dev
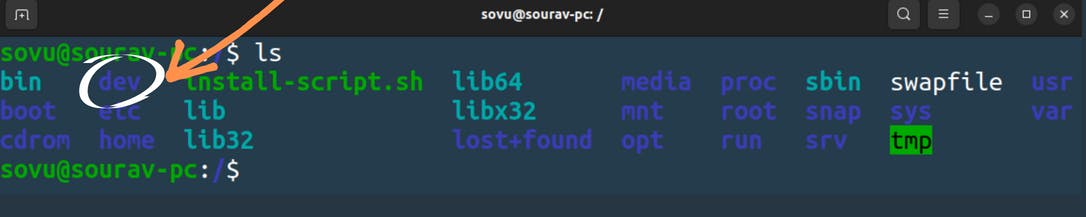 Earlier I mentioned that even devices in our system are files hard drives, printers, and cd-roms you want to see them they’re in the dev directory. dev stand for devices let “ls” dev
Earlier I mentioned that even devices in our system are files hard drives, printers, and cd-roms you want to see them they’re in the dev directory. dev stand for devices let “ls” dev
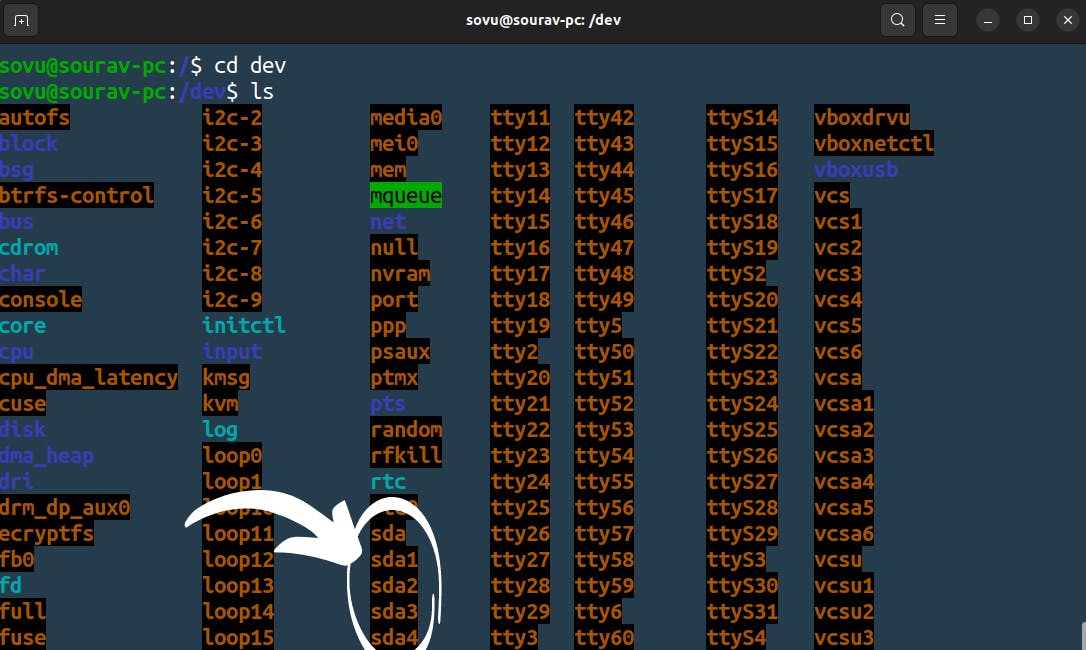 that’s a lot of files we could spend all day here but we’re not going to we’re going to look at one thing sda and sda1 those right now are our hard drives. that’s the disk it's the file which means we can cat that file but I’m not going to do that because that’s a very big file load.
that’s a lot of files we could spend all day here but we’re not going to we’re going to look at one thing sda and sda1 those right now are our hard drives. that’s the disk it's the file which means we can cat that file but I’m not going to do that because that’s a very big file load.
/etc
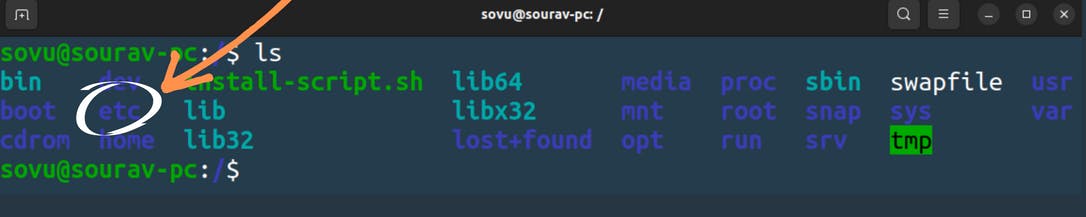 Now I also mentioned that the setting of your Linux server or your Linux computer files things like your network setting are stored inside a file and this kind of file is stored in an etc directory which stands for etcetera but people mainly call it etsy file
Now I also mentioned that the setting of your Linux server or your Linux computer files things like your network setting are stored inside a file and this kind of file is stored in an etc directory which stands for etcetera but people mainly call it etsy file
You will go a lot because configuration files of your system are here as well as some applications they can throw some stuff in there too.
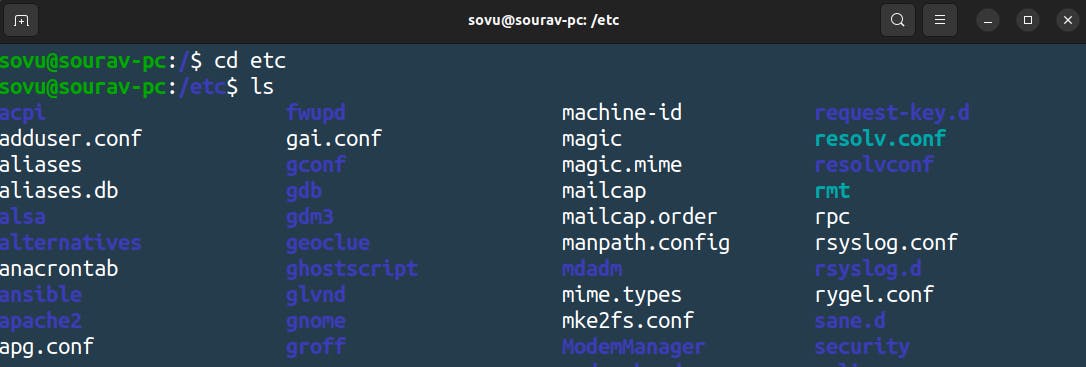 There are also many files and configurations there but we are going to focus on one set of configurations let’s focus on networking. let's go and see in
There are also many files and configurations there but we are going to focus on one set of configurations let’s focus on networking. let's go and see in
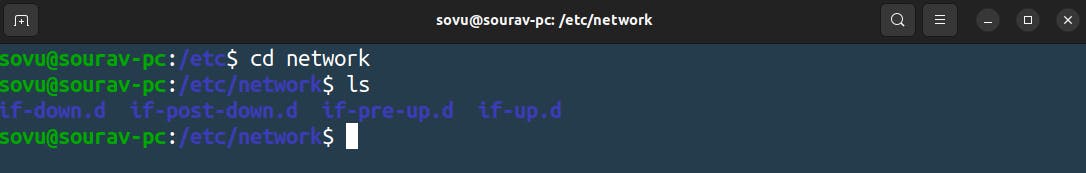
Unfortunately, the interface file is not there in the system for some reason which I don't but I will find out what's the problem.
Interface
Here are your network's interfaces and they’re assigned ip addresses this is where they’re configured pretty coolly and if you wanted to change your network settings you would often go into this file and just change it here. Now things do work differently on some Linux systems nowadays but this was a common way to do it and is still the common way to do it on some systems.
/mnt and media
 They both do the same thing they mount drives if you plug in a USB flash drive into your Linux box here it will automatically and automatically be mounted to the media directory as a file because everything’s a stinking file remember so media is mainly for your system mounting things automatically for you
They both do the same thing they mount drives if you plug in a USB flash drive into your Linux box here it will automatically and automatically be mounted to the media directory as a file because everything’s a stinking file remember so media is mainly for your system mounting things automatically for you
whereas the mnt directory also has drives mounted to it but drives you might mount manually you would actually use commands to mount a drive and again that would be represented as a file in the mnt directory.

